Throughout the year, there is an ongoing effort to raise awareness about breast cancer, however, in October, this effort is heightened as people dress in pink to display their unity and backing for those affected by the disease.
Introduction
Breast cancer affects predominantly women, characterized by exponential and abnormal growth in breasts cells (lobules, ducts, or connective tissue). Ductal and lobular cancer of the breast are most common. As the cancer progresses in stages, the cancerous cells spread to various body parts. If detected earlier and with early treatment, the earliest form of breast cancer is not life-threatening.
Risk Factors
They range from environmental factors, habits of an individual, and genetic factors. Some of the well established risk factors for breast cancer are:
- Age: The incidence increases in the age group of 35 to 50 years. Among younger females, there is an increasing incidence of aggressive type of breast cancer, which can be tackled by promoting early detection and advocacy for younger females
- Family history: If breast cancer was seen before menopause in the mother and sisters.
- Parity: Evidence shows women with early, first full-term pregnancies had relatively lower risk.
- Age related to Menarche and Menopause of women: Early menarche and late menopause is a fixed risk factor.
- Hormonal Factors: Hormones (estrogen stimulates abnormal division of the breast tissue and progesterone masks the cancer cells from the body’s immune system) play crucial roles in the development of breast cancer.
- Socioeconomic status: Linked positively with higher economic groups at high risk due to late first birth in this strata.
- Diet: high-fat diet and obesity are linked positively.
- Others: Radiation exposure, Tobacco, and oral contraceptives.
Signs and Symptoms
Early signs
- Painless, firm breast lump or mass.
- Changes in the size or shape.
- Pain in the breast or nipple that is continual and unaccountable.
- Abnormal discharge or bloody discharge can be a warning sign.
Other signs and symptoms
- Dimpling or puckering of the skin on the breast.
- Redness and warmth on touch, sometimes darkish breast skin.
- Inverted nipple.
- Nipple or skin over the breast has flaking skin or peeling skin.
- Growth in size or inflaming lymph nodes in nearby armpits or adjacent collarbone (beauty bone).
- Weight loss.
Significance of self-examination and Regular Screening
- Helps to identify breast abnormalities at an early and treatable stage.
- Helps to improve survival rates
- Less aggressive treatment, reducing the need for extensive surgeries, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy
- Helps women to live a quality life
- Allows healthcare providers to tailor treatments to the specific stage leading to more effective care
- It can reduce healthcare costs
- It can provide peace of mind
- Risk of breast cancer assessment
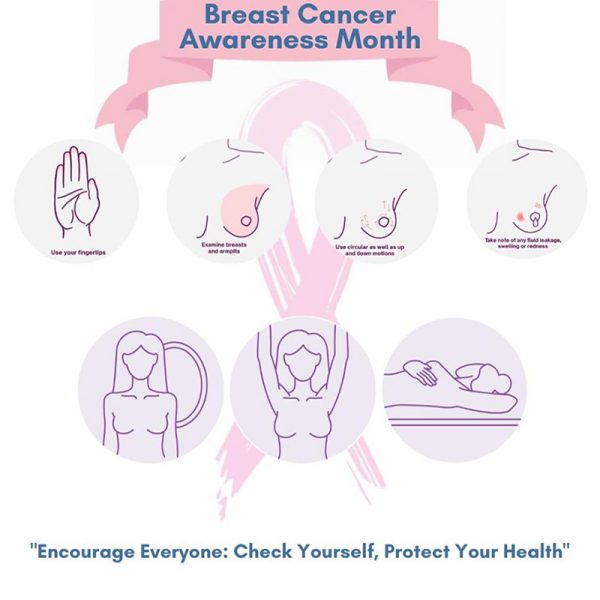
Breast self-examination
While taking a Shower
- Remember to touch and check the entirety of both breasts and under arms, for this use pads of 3 middle fingers of your hands with firm but light, medium comfortable pressure on these areas.
- Every month you must check for any changes like lumps, thickening, knots, etc in both breast and armpits.
Stand facing the mirror
- Raise your arms at the side, look at your breasts for changes in the outlines of the breast, its shape. Check for any dimple, enlargement in skin tissue in the whole breast and nipples.
- Now with palms firmly on your hips, squeeze your chest muscles. Then look for any changes like dimples, abnormal wrinkles in the skin.
Lay on bed with face towards ceiling
- With your left arm behind your head like in the picture below, use your right hand fingers to move around your left breast in a firm and light comfortable manner as discussed for “while taking a shower”feel for abnormality in breast and under arm. Use fingers in a circular and up down motion manner to check.
- Look for abnormalities like lumps under skin, thickenings of skin, and any hard knots around breast tissue or under arm.
- Pinch or squeeze the nipple in a manner that if any abnormal liquid discharge is to be found.
- Now repeat similarly for the other side, this time right arm will be behind your head and you will check for abnormality in right breast with your left hand.
Importance of Awareness and Education
- Awareness campaigns can promote self-examinations and mammograms to detect cancer would increase the opportunistic screening rates
- Helps to recognize the symptoms, seek medical care, adequate treatment, better quality of life, and improved survival
- Reduce breast cancer mortality rates
- Adoption of preventive measures, reducing risk factors, and improved lifestyle choices
- Help communities understand the disease better and offer meaningful support to patients and survivors
- Breast cancer awareness can lead to improving healthcare policies, screening programs, and funding for research
- Build community support
- Encourages people to take responsibility for their own breast health
Research and treatment developments
- Tailoring breast cancer treatments to each patient’s tumor has reduced side effects and improved treatment effectiveness.
- Ongoing research in breast cancer immunotherapy brings hope for patients with treatment options as it utilizes the immune system to fight against the disease.
- Advancements in mammography, risk assessment, and imaging technology have significantly improved detection, leading to better prognosis.
- Survivorship care now addresses the needs and emotional and social well-being of survivors, helping them lead fulfilling lives post-treatment.
- Access to statistics empowers patients and healthcare providers by enabling them to make decisions and take proactive measures for treatment.
- Breast cancer research is significantly propelled by trials that continually expand our knowledge base and provide various treatment options.
- Community campaigns support networks that bring together families, caregivers, survivors, and patients to provide resources and emotional assistance for individuals facing breast cancer challenges.
- A crucial part of cancer care is palliative care, which aims to enhance the quality of life for patients and their families.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices for Breast Cancer Prevention
- Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins should be in your diet. They provide all the nutrients you need to stay healthy and lower your risk of breast cancer. All while doing the same for your antioxidants.
- Don’t let things get too relaxed; staying physically active will help you maintain a healthy weight and improve your immune system’s defense against breast cancer. Something as simple as a walk around the block is enough.
- Keep an eye on your numbers, especially after menopause. Excess fat isn’t suitable for your body, including increasing the risk of breast cancer.
- Excess consumption of alcohol increases the risk of getting breast cancer.
- It’s been known that smoking causes many types of cancers, including breast cancer. To ensure you have a future without worrying about cancer, quit smoking as soon as possible.
- Regular check-ups make sure we stay on track with our health. Simple tests like mammograms and clinical breast exams sound scary, but they can catch something early on and treat it more effectively. In turn, we are improving our chances.
- Stress is the devil of our well-being. It weakens our immune system and even leads to health problems. The easiest way to manage stress is through meditation and yoga. It doesn’t just lower stress but makes us feel better overall.
- When people say sleep is important, they mean it. 7 to 9 hours per night is what we should aim for to maintain a healthy body and mind. Sleep deprivation can cause hormone levels to go out of balance and even increase your cancer risk.
- Trust your support system when you need help during tough times. It’s not always easy doing everything alone, so don’t be afraid to lean on friends, family, and support groups because they’re there for you
Global Health Initiatives & Campaigns
World Health Organization
- Global Breast Cancer Initiative (GBCI) was founded by the World Health Organization in 2021, with the main goal of reducing the mortality of global breast cancer. This initiative focuses on enhancing access to early breast cancer detection measures, ensuring timely comprehensive cancer management, and implementing practical and sustainable approaches tailored to the specific contexts and resources available in Low- and Middle-Income Countries (LMICs).
- Additionally, it is recommended to conduct monitoring and evaluation of these interventions before scaling up programs. The involvement and investment of advocacy groups, stakeholders, and policymakers are strongly encouraged to foster greater participation and ensure the sustainability of the program.
The National Health Mission (NHM)
- It is implementing the National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases and Stroke (NPCDCS) for activities up to the district level.
Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY)
- It is being implemented under the auspices of Ayushman Bharat to lessen the financial burden for poor and vulnerable groups arising out of catastrophic hospital episodes and to provide access to quality health services.
Ayushman Bhav
- The ‘Ayushman Bhav’ initiative aims to extend healthcare services to every village and town in line to provide healthcare access to every stratum of society. It encompasses a series of interventions, including Ayushman Melas. The increasing burden of non-communicable diseases (NCDs), resurging diseases, injuries, and road traffic accidents (RTAs) necessitates urgent and concrete efforts.
- In 2018, the Indian Government launched its flagship program “Ayushman Bharat” which aims to achieve Universal Health Coverage (UHC). It has 4 pillars, one of them is the Health & Wellness Centre (AB-HWC). Under AB-HWC, Health Melas is organized to provide awareness, early diagnosis through screening, comprehensive primary healthcare services, community-based risk assessment, and population-based screening for diseases such as diabetes, common cancers including breast and cervical cancer, and tuberculosis.
Conclusion
In Modern times, the global focus on breast cancer has escalated due to its rising prevalence and mortality rate. Various factors contribute significantly to the risk of developing breast cancer. Early detection through self-examinations and regular screenings remains an important element in combating the disease, as it allows for less intrusive treatments and improved survival rates. The evolving aspect of personalized therapies, targeted medications, and immunotherapy offers hope for more effective and customized treatment plans. Furthermore, initiatives like the Global Breast Cancer Initiative (GBCI) and national programs such as ‘Ayushman Bhav’ in India aim to build up awareness, promote early detection, and ensure accessible and comprehensive breast cancer management, especially in low- and middle-income countries. These efforts underscore the importance of education, prevention through a healthy lifestyle, and community engagement in the fight against breast cancer.
References
- Akram, M., Iqbal, M., Daniyal, M., & Khan, A. U. (2017). Awareness and current knowledge of breast cancer. Biological Research, 44(1), 26. https://biolres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40659-017-0140-9
- Ayoola, T. (2022, October 14). Why is breast cancer awareness important? MyCHN Community Health Network. https://mychn.org/why-is-breast-cancer-awareness-important/
- Ayushman Bhav, Government of India (2023) https://ayushmanbhav.mohfw.gov.in/
- Breast cancer. Basic information. Cancer Home. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/breast/ https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/breast/basic_info/what-is-breast-cancer.htm
- Breast self-examination – Steps, purpose, importance & advantages. (2022, October 19). https://www.pacehospital.com/breast-self-examination
- Brenner, D. R., Brockton, N. T., Kotsopoulos, J., Cotterchio, M., Boucher, B. A., Courneya, K. S., … & Friedenreich, C. M. (2016). Breast cancer survival among young women: A review of the role of modifiable lifestyle factors. Cancer Causes & Control, 27(11), 1393-1410. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26970739/
- Dharsee, N., Mwakatobe, K., Haule, M., Tarimo, Q., & Mbwana, M. (2023). Needs and opportunities for information in patients with metastatic breast cancer attending a tertiary hospital in Tanzania—A qualitative study. Advances in Breast Cancer Research, 12(3), 63–76. https://doi.org/10.4236/abcr.2023.123006. https://www.scirp.org/journal/paperinformation.aspx?paperid=125604
- Information, Education & Communication (IEC). (2020). mohfw.gov.in. https://main.mohfw.gov.in/sites/default/files/17563256478856633221.pdf
- Kryzak, A. (2023, August 4). Breast Self-Exam. National Breast Cancer Foundation. https://www.nationalbreastcancer.org/breast-self-exam/
- Park, K. (2023). Non-communicable diseases. Cancer. Volume 23. Risk factors.https://milonm28.files.wordpress.com/2017/08/parks-preventive-social-medicine-23rd-ed.pdf
- Kryzak, A. (2023). Breast cancer signs and symptoms. National Breast Cancer Foundation. https://www.nationalbreastcancer.org/breast-cancer-symptoms-and-signs/
- Naghavi-Behzad, M., Gerke, O., Kodahl, A. R., Vogsen, M., Asmussen, J. T., Weber, W., Hildebrandt, M. G., & Kidholm, K. (2023). Cost-effectiveness of 2-[18F]FDG-PET/CT versus CE-CT for response monitoring in patients with metastatic breast cancer: a register-based comparative study. Scientific Reports, 13(1), 16315. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-43446-7
Pietrangelo, A. (2022, January 6). What are the early signs and symptoms of breast cancer? Healthline.https://www.healthline.com/health/breast-cancer/warning-signs#other-causes-of-breast-pain - Petrova, D., Garrido, D., Zuzana Špacírová, Nicolás Francisco Fernández-Martínez, Ivanova, G., Rodríguez‐Barranco, M., Pollán, M., Rocío Barrios‐Rodríguez, & María José Sánchez. (2022).
Duration of the patient interval in breast cancer and factors associated with longer delays in low‐and middle‐income countries: A systematic review with meta‐analysis. Psycho-Oncology, 32(1), 13–24. https://doi.org/10.1002/pon.6064 - Pippin, M. M. (2023, January 23). Breast Self-Examination. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK565846/
- Katira, K. (2023, October 10). Importance of early detection in breast cancer | Breast Cancer Awareness Month. WION https://www.wionews.com/entertainment/lifestyle/news-importance-of-early-detection-in-breast-cancer–breast-cancer-awareness-month-643713
- World Health Organization: WHO & World Health Organization: WHO. (2023). Breast cancer. www.who.int. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/breast-cancer
- World Health Organization (2023), Global Breast Cancer Initiative Implementation Framework Assessing, strengthening and scaling up services for the early detection and management of breast cancer. ISBN: 978-92-4-006598-7 https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240065987
- Press Information Bureau, Government of India. https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetailm.aspx?PRID=1670707#:~:text=National%20harmaceutical%20Pricing%20Authority%20
Written by
Janhvi Sahai, Madhuri Bhatt, Nidhi S Pillai, Priyanka Malla, Sushmi Wilson













Leave A Comment